Sector Results and Learning:
Transportation
This Transportation Sector Results and Learning page is a repository of evidence generated by all MCC-funded transportation interventions. To promote learning and inform future program design, this page captures monitoring data from key common indicators, showcases recent and relevant evaluations, includes all agency lessons from completed transportation evaluations to-date, and links to learning that has been aggregated across completed evaluations in the sector.
What Do We Invest In?
MCC has funded $3.3 billion in transportation interventions as of September 2024. These interventions fall into the following categories: transportation infrastructure; management, funding, operations and maintenance assistance; and transportation policy, regulatory, planning, financing and institutional development assistance.
-
Management, Funding, Operations and Maintenance Assistance
 These programs focus on building the capacity of local transportation public agencies/institutions to increase funding sources and cost-effectively manage, operate and maintain transportation systems.
These programs focus on building the capacity of local transportation public agencies/institutions to increase funding sources and cost-effectively manage, operate and maintain transportation systems. -
Transport Infrastructure
 These programs focus on the upgrading, improvement, rehabilitation and maintenance of transportation infrastructure such as roads, ports and airports to reduce transportation costs.
These programs focus on the upgrading, improvement, rehabilitation and maintenance of transportation infrastructure such as roads, ports and airports to reduce transportation costs. -
Transport Policy, Regulatory, Planning, Financing and Institutional Development Assistance
 These programs focus on building the capacity of local transportation public agencies/institutions to set policies and build planning and implementation capacities to keep transportation costs low.
These programs focus on building the capacity of local transportation public agencies/institutions to set policies and build planning and implementation capacities to keep transportation costs low.
What Have We Completed So Far?
MCC and its country partners develop and tailor Monitoring and Evaluation Plans for each program and country context. Within these country-specific plans, MCC uses common indicators to standardize measurement and reporting within certain sectors. See below for a subset of common indicators that summarize implementation achievements across all MCC transportation investments as of September 2024.
-
4,813
kilometers of roads that have been contracted for design work
-
4,281
kilometers that have been contracted for road works
-
3,862
kilometers of roads completed
What Have We Achieved?
MCC commissions independent evaluations, conducted by third-party evaluators, for every project it funds. These evaluations hold MCC and country partners accountable for the achievement of intended results and also produce evidence and learning to inform future programming. They investigate the quality of project implementation, the achievement of the project objective and other targeted outcomes, and the cost-effectiveness of the project. The graphs below summarize the composition and status of MCC’s independent evaluations in the transportation sector as of November 2024. Read on to see highlights of published interim and final evaluations. Follow the evaluation links to see the status of all planned, ongoing, and completed evaluations in the sector and to access the reports, summaries, survey materials, and data sets.
Highlighted Evaluations
-
 Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Mozambique Compact that rehabilitated two primary national road segments in Mozambique: the Namialo-Rio Lurio Road (149.7 km) and Nampula-Rio Ligonha Road (103 km).
Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Mozambique Compact that rehabilitated two primary national road segments in Mozambique: the Namialo-Rio Lurio Road (149.7 km) and Nampula-Rio Ligonha Road (103 km). -
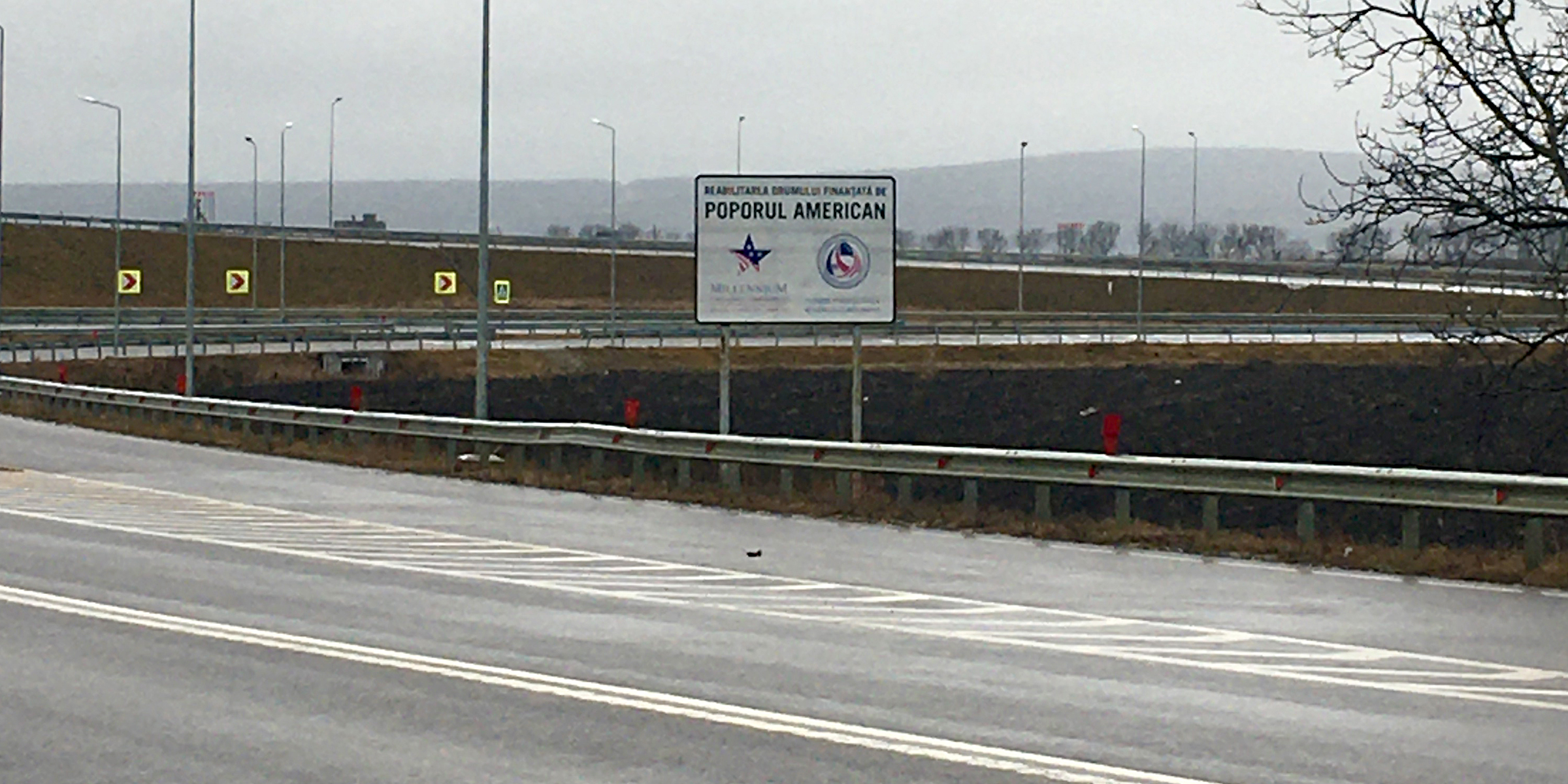 Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Moldova Compact that aimed to rehabilitate a 93 kilometer portion of the national M2 Road, including associated structures such as bridges, drainage systems, and culverts.
Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Moldova Compact that aimed to rehabilitate a 93 kilometer portion of the national M2 Road, including associated structures such as bridges, drainage systems, and culverts. -
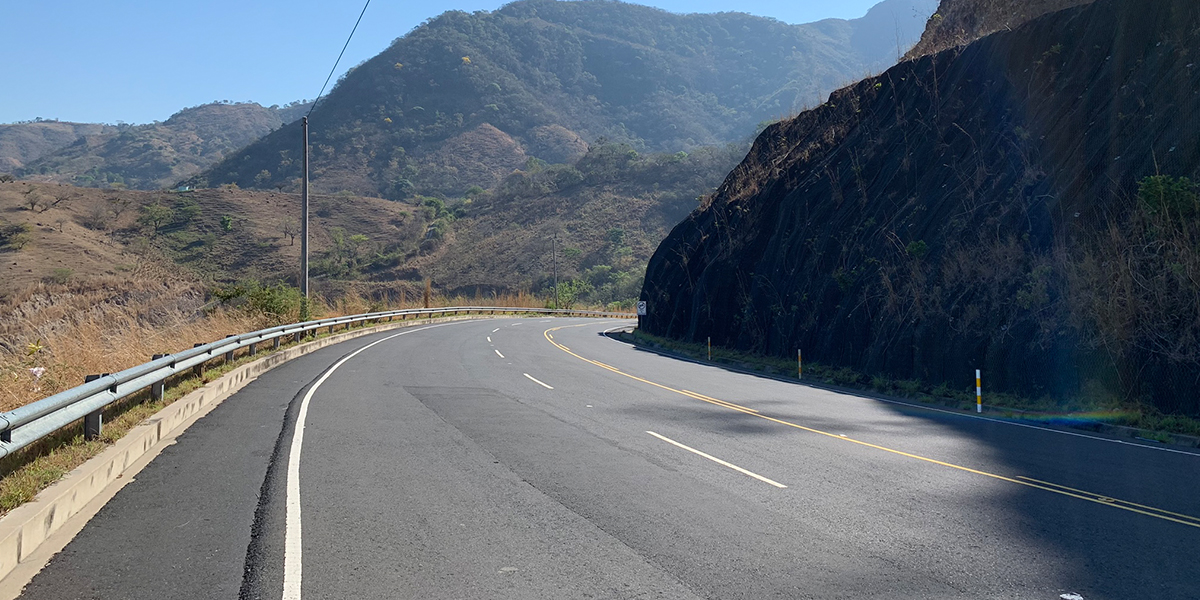 Learn the final results of a project from MCC’s El Salvador Compact that aimed to connect El Salvador’s northern zone with the rest of the country by improving roads, lowering transportation costs, and decreasing travel times.
Learn the final results of a project from MCC’s El Salvador Compact that aimed to connect El Salvador’s northern zone with the rest of the country by improving roads, lowering transportation costs, and decreasing travel times. -
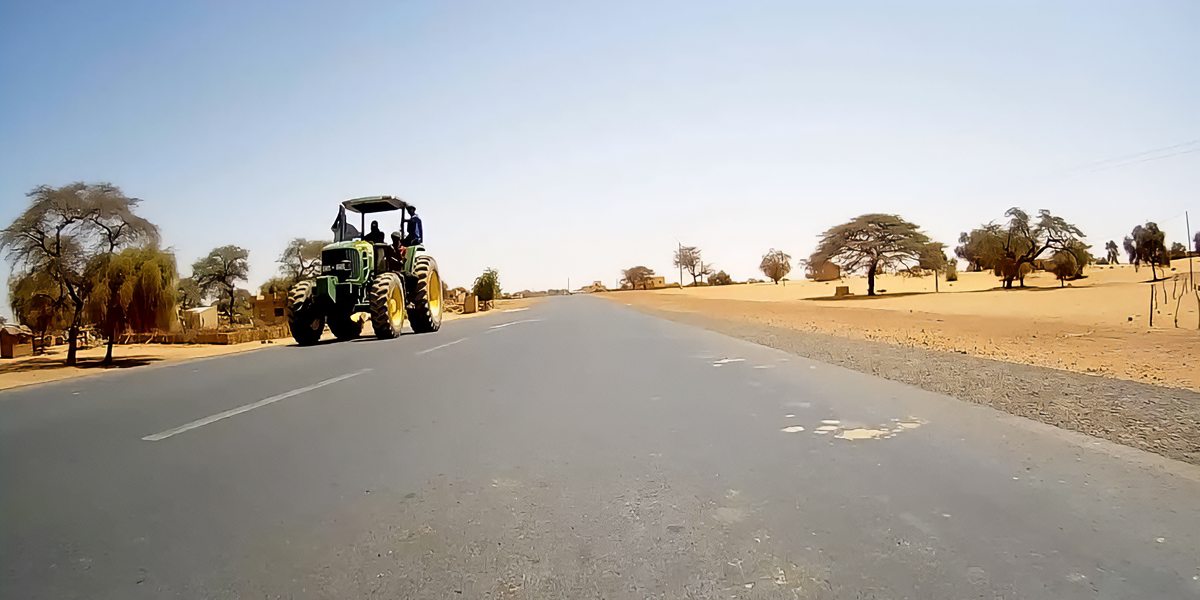 Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Senegal Road Rehabilitation Project that was designed to boost economic growth by unlocking the country’s agricultural productivity and expanding access to markets and services.
Read this Evaluation Brief to learn the results of a project from MCC’s Senegal Road Rehabilitation Project that was designed to boost economic growth by unlocking the country’s agricultural productivity and expanding access to markets and services.
What Have We Learned from Our Results?
To link the evidence from the independent evaluations with MCC practice, project staff produce an MCC Learning document at the close of each interim and final evaluation to capture practical lessons for programming and evaluation. Use the filters below to find lessons relevant to your evidence needs.
Filter By
How Have We Aggregated Learning Across the Sector?
MCC has developed a Principles into Practice paper using evidence from completed independent evaluations in the transportation sector – Principles into Practice: Lessons from MCC’s Investments in Roads. The Principles into Practice series offers a frank look at what it takes to make the principles MCC considers essential for development operational in the projects in which MCC invests. The learning captured in this paper informs MCC’s ongoing efforts to refine and strengthen its own model and development practice in the transportation sector. MCC hopes this paper will also allow others to benefit from, and build upon, MCC’s lessons.

