-
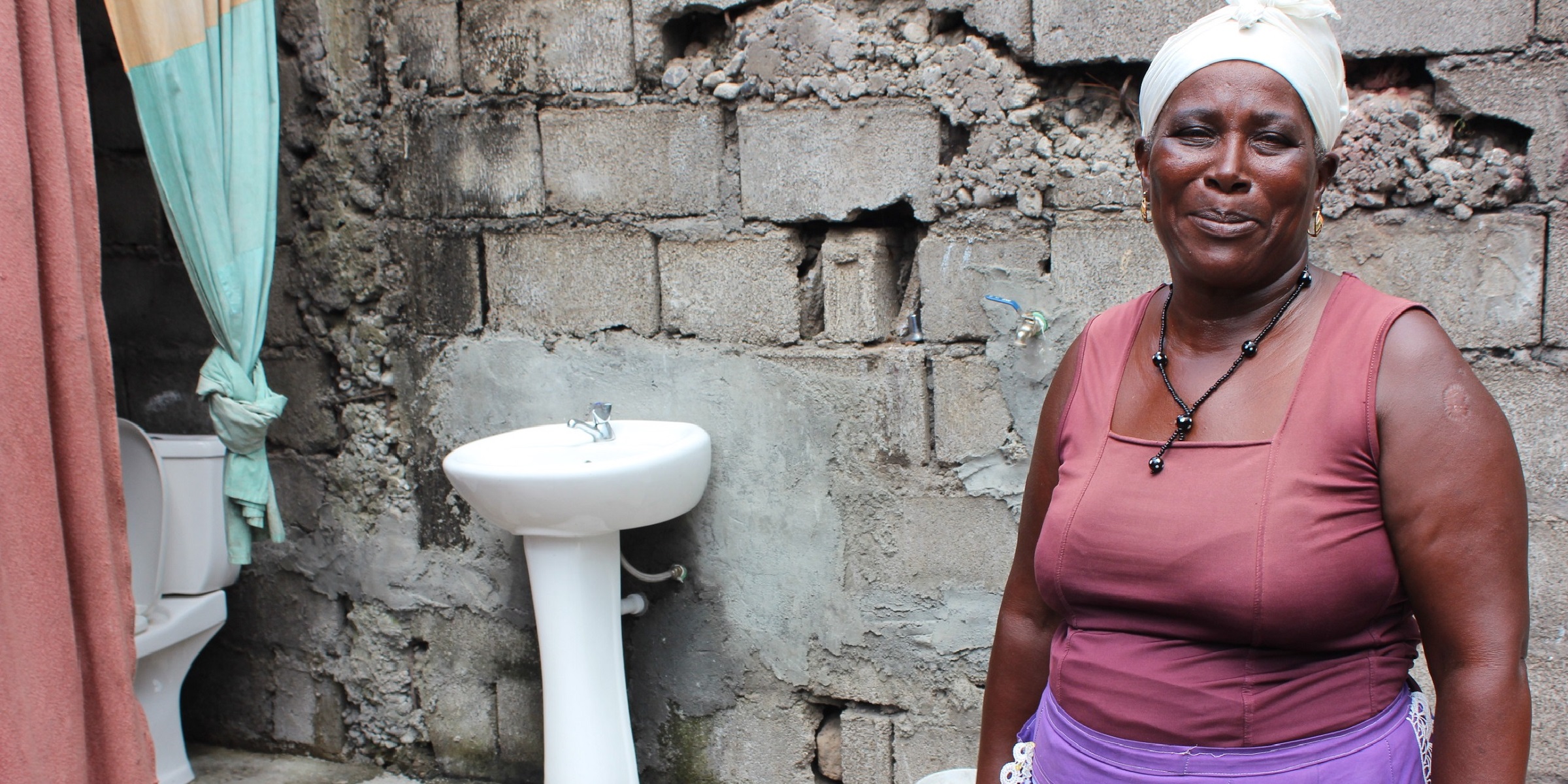
MCA-Cabo Verde II
Thanks to the Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Project within the Cabo Verde II Compact, which provided low-cost household connections to water and sanitation networks, 43 percent more households have piped water relative to before the compact and twice as many have a sewer connection.
-
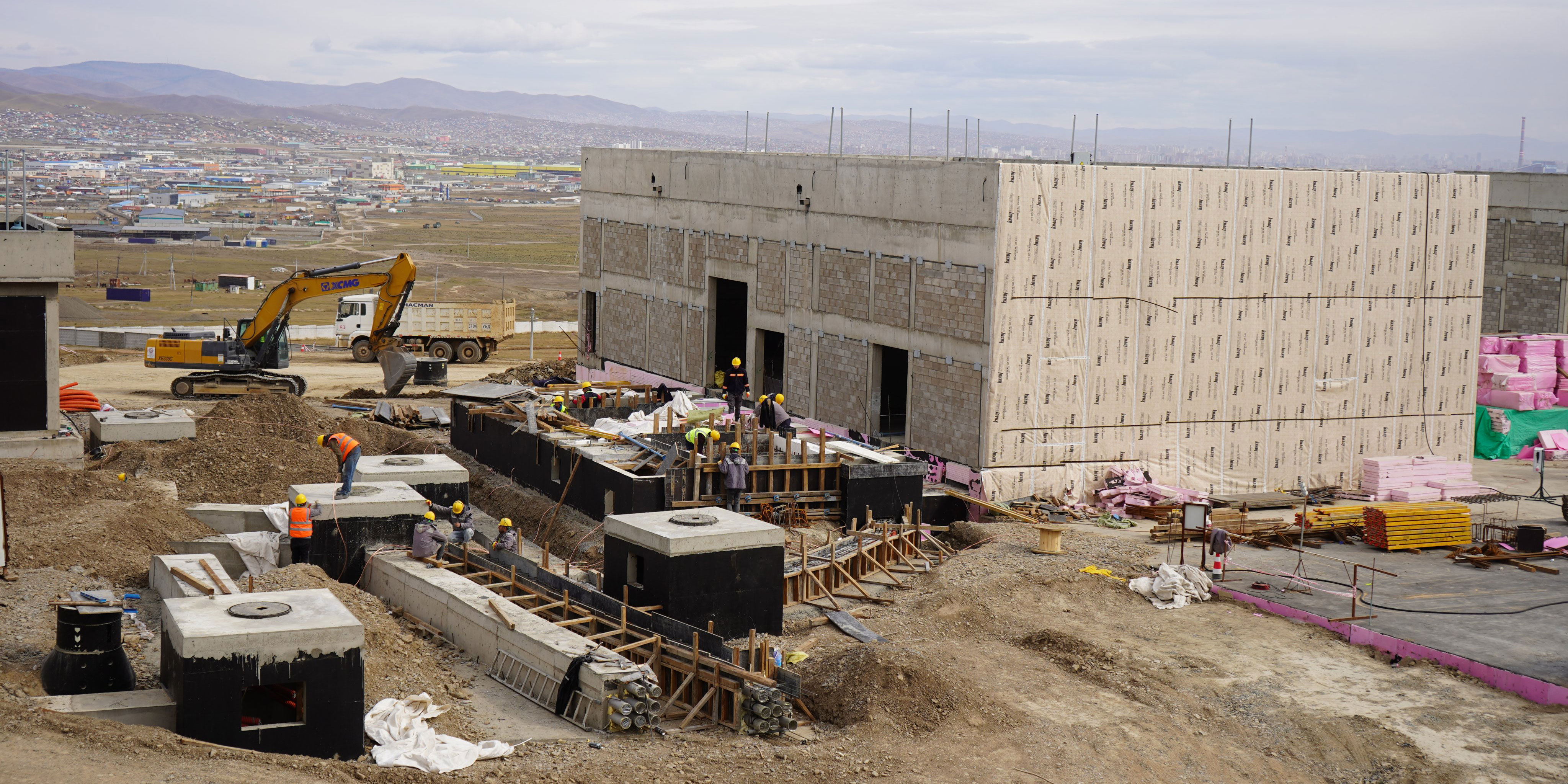

MCA-Mongolia
The population of Mongolia’s capital, Ulaanbaatar, nearly tripled in the last three decades. To meet the city’s demand for water, MCC’s Mongolia Water Compact is investing in infrastructure to increase Ulaanbaatar's water supply, including new groundwater wells, a state-of-the-art drinking water purification plant, and a new wastewater treatment plant.
-
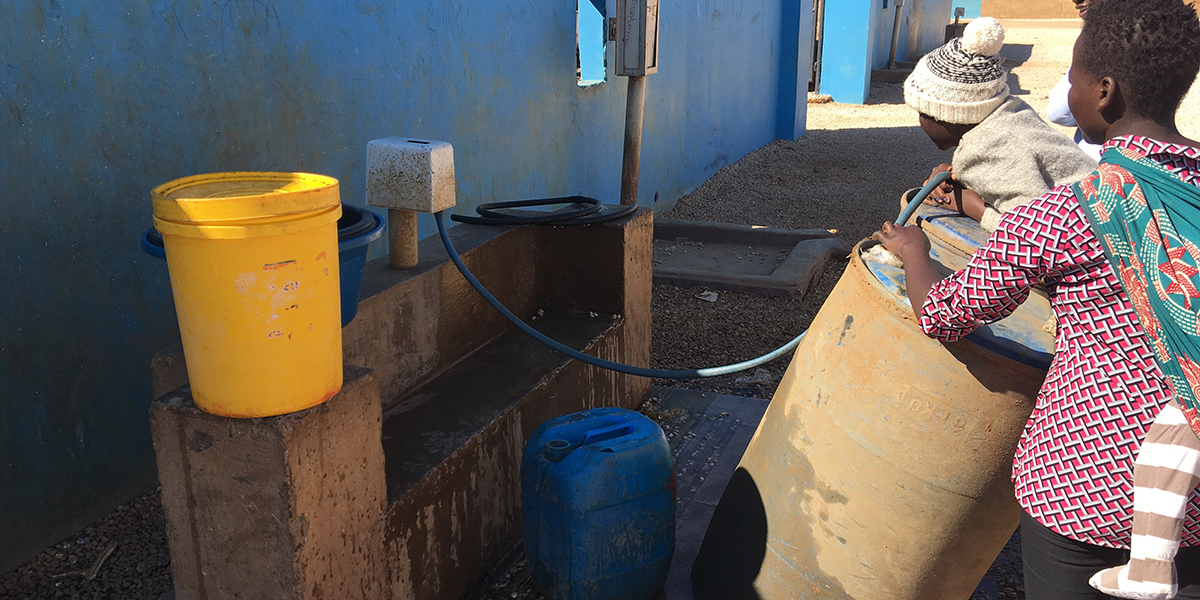

MCC
Women and girls often suffer disproportionately from a lack of access to clean water and adequate sanitation. To address inequalities, MCC’s Zambia Compact prioritized social and gender integration while investing in major infrastructure improvements in the capital of Lusaka. The compact expanded Lusaka's sewage network, improved the city's storm-water drainage, and connected more than 12,000 new customers to the piped water network.
-

MCC
Limited access to clean drinking water and quality sanitation infrastructure contributes to Timor-Leste’s high incidence of water-borne diseases. The MCC Timor-Leste Compact will introduce the country’s first centralized sanitation and wastewater treatment system and improve related drainage. The compact will supply disinfected water to 429,000 residents in Dili and 64,000 residents in the surrounding area.
-
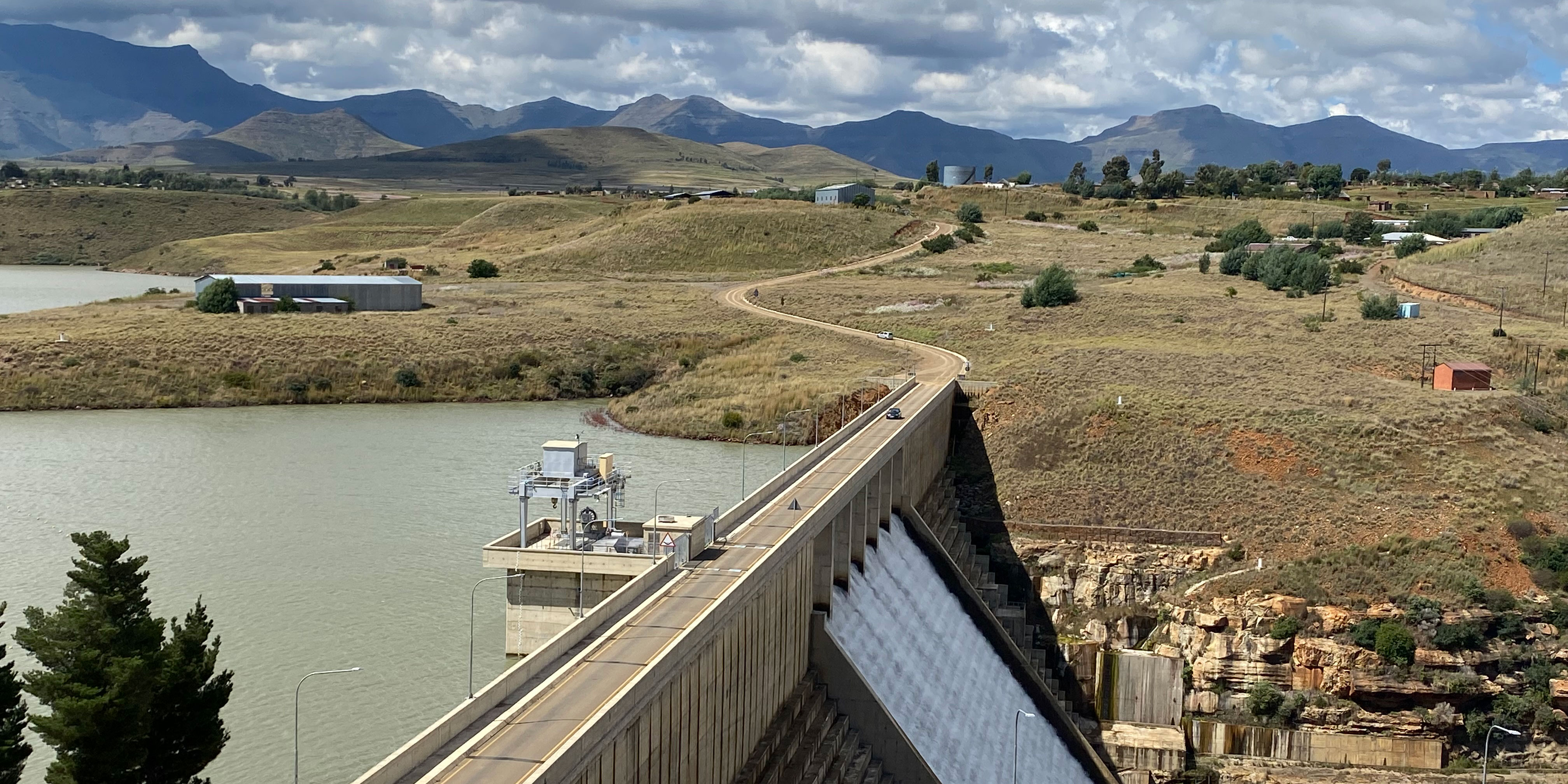

Jessica Glickman, MCC
The Government of Lesotho and MCC partnered to support Lesotho’s vision to provide secure, adequate, sustainable and clean water supply and sanitation services to rural and urban consumers. Through the Lesotho Compact, the water supply to Maseru and the surrounding areas increased and water collection outside the home was virtually eliminated.
-
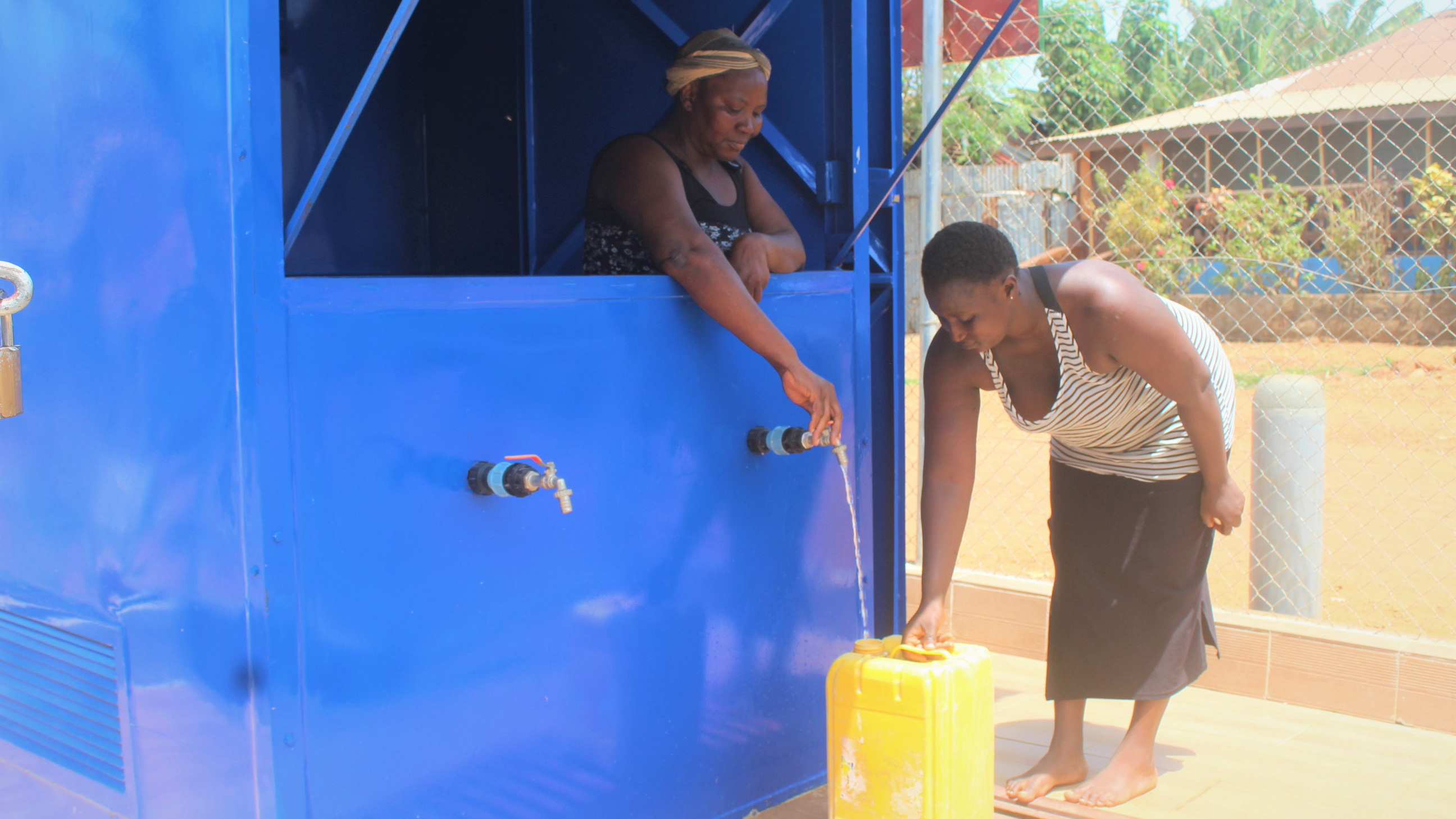

MCCU Sierra Leone
MCC’s Sierra Leone Threshold Program (2016-2021) activities included installing new water pipes and water distribution kiosks, like the one pictured above, in the capital city of Freetown. An $8 million Regulatory Strengthening Project aimed to build the capacity of the new regulator, improve sector governance, and support long-term financial sustainability of the water sector. In 2021, the regulator approved Guma’s first tariff increase in five years using policies developed under the threshold program.
MCC builds large-scale infrastructure and supports policy and institutional reforms that help partner governments more effectively deliver critical water and sanitation services to their people. MCC works with its partner countries to identify and design projects that provide sustainable, affordable, and reliable access to water for families, businesses, farmers, and energy-generating national utilities.

